
Structures and Dynamics of Ultra-thin Smectic Films
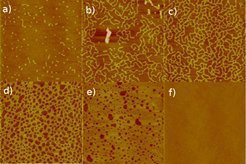
Fig 1: AFM height images (area 20 x 20 μm2) of ultra-thin (two to three molecular layers) smectic films spin coated from solution onto silicon wafers. The concentration of the smectic compound (8CB) in the spin-coating solution was 2.8 mg/ml (a), 3.0 mg/ml (b), 3.2 mg/ml (c), 3.4 mg/ml (d), 3.6 mg/ml (e), and 3.8 mg/ml (f). The images demonstrate the partial formation of the smectic top layer: with increasing concentration, a structural sequence is observed which starts with isolated islands which grow to a porous structure and finally form a complete layer. The height difference between the thicker and the thinner parts of the film is about 3.2 nm, corresponding to the thickness of one molecular smectic layer.
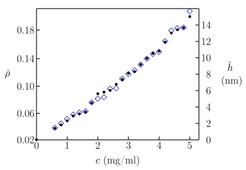
Fig. 2: Mean film thickness, as determined by ellipsometry (black dots, left axis: ellipticity coefficient ρ, right axis: resulting mean thickness h) and by analyzing the AFM images (blue diamonds, right axis only), as function of the concentration c of the liquid crystal compound 8CB in the spin coating solution.

Image processing enables the determination of the trajectories of the probe molecules and from the mean square displacement the diffusion coefficient is obtained.



