
Introduction
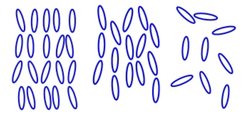
Fig. 1: Schematic drawings of the smectic (left), nematic (middle), and isotropic (right) state
![Fig. 2: Temperature dependence of the ellipticity coefficient ρ of the free surface of a liquid crystal illustrating a possible logarithmic divergence of the thickness of a layer-by-layer growing smectic surface phase; TAIdesignates the temperature of the smectic-A − isotropic bulk transition. Each step corresponds to the formation a molecular smectic layer at the surface. [R. Lucht, Ch. Bahr, G. Heppke, J. Phys. Chem. B 102, 6861 (1998)].](/3205458/original-1518437627.jpg?t=eyJ3aWR0aCI6MjQ2LCJvYmpfaWQiOjMyMDU0NTh9--c0a09d53f7311d966ef61b5389087ca63e075af4)
Fig. 2: Temperature dependence of the ellipticity coefficient ρ of the free surface of a liquid crystal illustrating a possible logarithmic divergence of the thickness of a layer-by-layer growing smectic surface phase; TAIdesignates the temperature of the smectic-A − isotropic bulk transition. Each step corresponds to the formation a molecular smectic layer at the surface. [R. Lucht, Ch. Bahr, G. Heppke, J. Phys. Chem. B 102, 6861 (1998)].
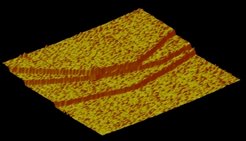
Fig. 3: AFM image of smectic-A layers spreading on a silicon wafer. The area is about 10 x 10 μm2, the height of the three layer steps amounts to 3 nm which corresponds to the smectic layer thickness of the compound under investigation (8CB).



![Fig. 2: Temperature dependence of the ellipticity coefficient ρ of the free surface of a liquid crystal illustrating a possible logarithmic divergence of the thickness of a layer-by-layer growing smectic surface phase; TAIdesignates the temperature of the smectic-A − isotropic bulk transition. Each step corresponds to the formation a molecular smectic layer at the surface. [R. Lucht, Ch. Bahr, G. Heppke, J. Phys. Chem. B 102, 6861 (1998)]. Fig. 2: Temperature dependence of the ellipticity coefficient ρ of the free surface of a liquid crystal illustrating a possible logarithmic divergence of the thickness of a layer-by-layer growing smectic surface phase; TAIdesignates the temperature of the smectic-A − isotropic bulk transition. Each step corresponds to the formation a molecular smectic layer at the surface. [R. Lucht, Ch. Bahr, G. Heppke, J. Phys. Chem. B 102, 6861 (1998)].](/3205458/original-1518437627.jpg?t=eyJ3aWR0aCI6ODQ4LCJmaWxlX2V4dGVuc2lvbiI6ImpwZyIsIm9ial9pZCI6MzIwNTQ1OH0%3D--7d2b400b8267ad29aad3d35f35f0d740c3ab863b)
